GLA and Cardiovascular Health
Cardiovascular Disease
According to World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular disease is caused by disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including heart attacks, atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension, congenital heart disease, peripheral arterial disease...etc. The major causes of cardiovascular disease are tobacco use, an unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and excessive use of alcohol.
According to World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular disease is caused by disorders of the heart and blood vessels, including heart attacks, atherosclerosis, stroke, hypertension, congenital heart disease, peripheral arterial disease...etc. The major causes of cardiovascular disease are tobacco use, an unhealthy diet, physical inactivity and excessive use of alcohol.
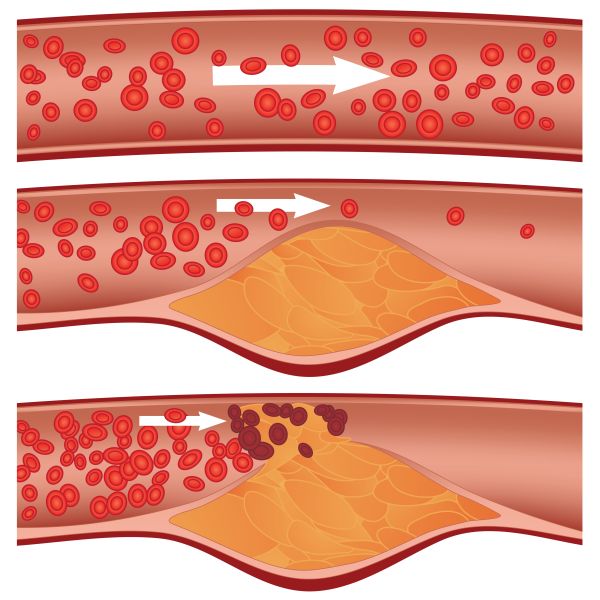
| Atherosclerosis is a common disorder that refers to the buildup of fats and cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein LDL) in and on your artery walls (plaques), which can restrict blood flow. It is largely the result of chronic, low-grade inflammation that causes degradation of the inner endothelial lining of the arteries. GLA and cardiovascular health GLA, through immediate conversion to DGLA inside the body, enhances PGE1 and 15-HETrE formation, which provide a good anti-inflammatory effect. Some of the GLA benefits on cardiovascular health include1-5:
|
 |
For difference between Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids on cardiovascular diseases, please click here.
References
- Fan YY et al. Importance of dietary gamma-linolenic acid in human health and nutrition. J Nutr 1998, 128: 1411-1414.
- Li JH et al. Cardioprotective effect of liposomal prostaglandin E1 on a porcine model of myocardial infarction reperfusion no-reflow. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 2011, 12: 638-643.
- Gupta V et al. PLGA microparticles encapsulating prostaglandin E1-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin complex for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Pharm Res 2011, 28: 1733-1749.
- Horrobin DF et al. How do polyunsaturated fatty acids lower plasma cholesterol levels? Lipids. Aug1983;18(8):558-62.
- Ishikawa T, et al. Effects of gammalinolenic acid on plasma lipoproteins and apolipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. Feb1989;75(2-3):95-104.

