
What are Essential Fatty Acids? What fatty acids are essential?
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) are essential nutrients that our bodies need but cannot build them on our own, so we must obtain them from food or health supplements. The two primary EFAs are α-linolenic acid (ALA) - an omega-3 fatty acid and linoleic acid (LA) - an omega-6 fatty acid, they are the building blocks for all the other fats in our bodies. EFAs are polyunsaturated fatty acids, which contain more than one double bond in their backbone and are considered as "good" fats, while saturated and trans- fatty acids are considered as 'bad" fats. Please note that, Oleic acid, a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid from olive oil, though healthy, is not essential.
Besides being the major sources of energy, EFAs are necessary to the healthy functioning of cell membranes by improving the membrane's flexibility and permeability as they are the main components of the cell membrane; they are also crucial for the synthesis of many important hormones and chemical messengers called eicosanoids.
Meet the Omega familiesWhat is "Omega"?
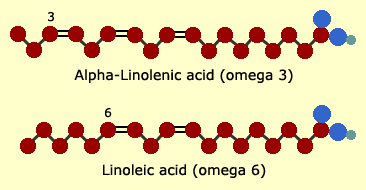
Typical fat molecules found in food are more than 12 carbons long. The beginning of the carbon chain of fatty acids is designated as the Alpha side, whereas the end of the chain is the Omega side.
Those polyunsaturated fatty acids that have their first double bond located in the third carbon from the end (the omega side) belong to omega-3 family. Similarly, in the case of omega-6 and omega-9 families, the first double bond appears in the sixth and ninth carbon from the end respectively.
Eicosanoids
Eicosanoids are a family of compunds that include prostaglandins (PG), prostacyclins (PGI), leukotrienes (LT), and thromboxanes (TX), the strongest and most important of which is prostaglandins (PG).
Eicosanoids are hormone-like substances that play an important role in regulating (either promoting or relieving) our bodies including inflammation, swelling, blood clotting, body temperature and allergic reactions...etc.
Eicosanoids are derived from 3 different 20-C long chain fatty acids:
- Dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA), an omega-6 fatty acid, gives rise to PGE1
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), an omega-3 fatty acid, gives rise to PGE3
- Arachidonic acid (AA), an omega-6 fatty acid, gives rise to PGE2
Series 1 and 3 Prostaglandins (PGE-1 & PGE-3) are anti-inflammatory while series 2 (PGE-2) are pro-inflammatory. The body must produce enough beneficial eicosanoids such as PGE1 and PGE3, otherwise the strong pro-inflammatory, blood-vessel-constricting, and blood-clotting effects of PGE2 will overwhelm the system.
Metabolic Pathway of Essential Fatty Acids

.jpg)
NOTE: * This is a rate-limiting process which is reduced by factors like ageing, Diabetes Mellitus, excessive alcohol consumption, medication, preservatives, stress, lack of sleep, high cholesterol level, malnutrition, viral infection and other diseases…etc.

